Keycloak provides simple integration with Spring applications. As a result, we can easily configure our Spring Boot API security to delegate authentication and authorization to a Keycloak server.
Prerequisites
- Docker Engine and Docker Compose (for running an example Keycloak instance), JDK and Maven (for running an example Spring Boot project).
- I’m working on a Spring Boot REST API that you can find in my
keycloak-spring-bootrepository. If you want to run the app locally, visit the project repository on GitHub and follow the directions in the README.md file. - My project contains Spring MVC tests that allow me to verify the security configuration. However, you can learn how to authorize Postman requests in Keycloak or configure Swagger UI to comply with the security setup to manually test your API.
- The solution that I’ll show works for the following sample client configuration:
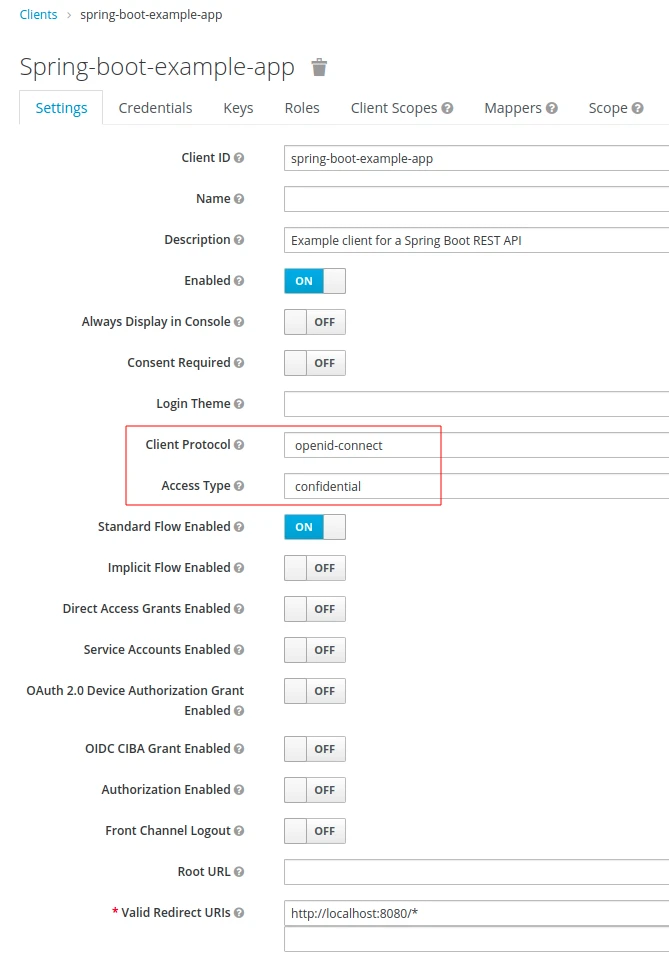
Securing Spring Boot applications with Keycloak
I’m going to add maven dependencies and required properties for Keycloak integration. Then, before I actually restrict access to my API endpoints, I will define a basic security configuration and test that both tools work together properly.
Add dependencies
First, I’m going to add the required dependencies to my project. In addition to the Keycloak and Spring Security starters for Spring Boot, I’ll add the Keycloak bom for adapters:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
<!-- pom.xml --> … <properties> … <keycloak-adapter.version>16.1.1</keycloak-adapter.version> </properties> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.keycloak.bom</groupId> <artifactId>keycloak-adapter-bom</artifactId> <version>${keycloak-adapter.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependencies> … <dependency> <groupId>org.keycloak</groupId> <artifactId>keycloak-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency> … </dependencies> … |
Add application properties
I’m running my Keycloak instance in a Docker container. For my sample client configuration, see the screenshot from the Prerequisites section.
I’m going to copy some information from my Keycloak client setup to the application.properties file:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# src/main/resources/application.properties keycloak.realm=keep-growing keycloak.resource=spring-boot-example-app keycloak.auth-server-url=http://localhost:8024/auth keycloak.credentials.secret=QjLCjk1I9sugcZSDFCsyAkoLOqAHDLKC |
Below is a brief explanation of the properties:
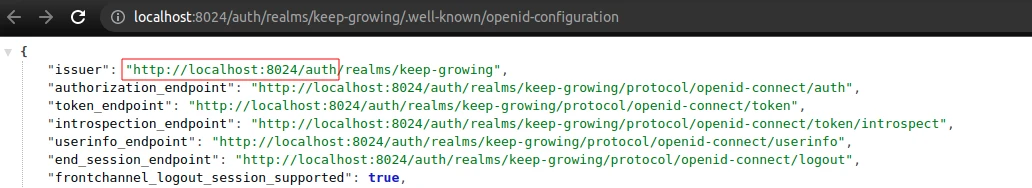
realm– my example realm name;resource– my example client name;auth-server-url– you can get the value from the Keycloak OIDC URI endpoint list by visiting the realm settings, clicking theOpenID Endpoint Configurationand copying theauthpath:
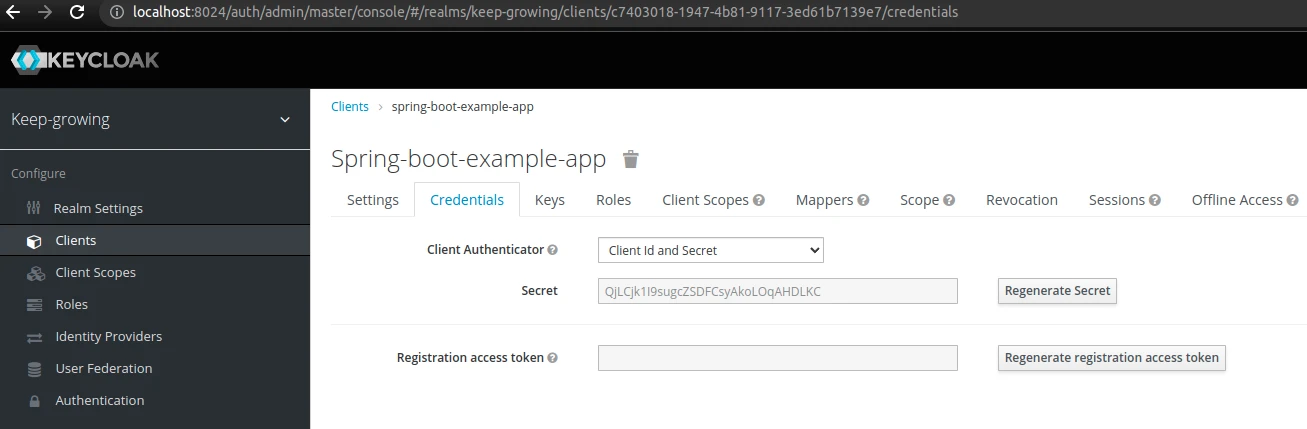
credentials.secret– my example client has theconfidentialaccess type. Therefore, I have to copy thesecretvalue from theCredentialstab:
If you want to access user roles at the client level and not user roles at the realm level, add the following property:
|
1 2 3 |
# src/main/resources/application.properties … keycloak.use-resource-role-mappings=true |
However, in my example I’m using realm roles for users.
Add security config
I’m going to create two configuration classes to handle my Keycloak setup.
The first one provides the ability to resolve my Keycloak config based on the application.properties file. I’m going to enclose it in a separate file to avoid the circular dependency issue (described in Javadoc in the snippet below):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
package in.keepgrowing.keycloakspringboot.security.config; import org.keycloak.adapters.KeycloakConfigResolver; import org.keycloak.adapters.springboot.KeycloakSpringBootConfigResolver; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * The {@code KeycloakConfigResolver} bean is not defined in a configuration class that extends * {@code KeycloakWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter} to avoid the {@code Circular References} problem in Spring Boot from version 2.6.0. * * @see <a href="https://github.com/keycloak/keycloak/issues/8857">Application don't start because of Circular Reference due to dependency injection</a> */ @Configuration public class KeycloakConfig { @Bean public KeycloakConfigResolver keycloakConfigResolver() { return new KeycloakSpringBootConfigResolver(); } } |
Next, I’m going to add the following class containing a Keycloak-based Spring security configuration:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
package in.keepgrowing.keycloakspringboot.security.config; import org.keycloak.adapters.springsecurity.KeycloakConfiguration; import org.keycloak.adapters.springsecurity.authentication.KeycloakAuthenticationProvider; import org.keycloak.adapters.springsecurity.config.KeycloakWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.mapping.SimpleAuthorityMapper; import org.springframework.security.core.session.SessionRegistryImpl; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategy; import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.session.SessionAuthenticationStrategy; import org.springframework.security.web.csrf.CookieCsrfTokenRepository; @KeycloakConfiguration //1 public class SecurityConfig extends KeycloakWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { //2 @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //3 super.configure(http); http .csrf().csrfTokenRepository(CookieCsrfTokenRepository.withHttpOnlyFalse()) .and() .authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().permitAll(); } @Autowired public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) { //4 auth.authenticationProvider(getKeycloakAuthenticationProvider()); } private KeycloakAuthenticationProvider getKeycloakAuthenticationProvider() { //5 KeycloakAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider = keycloakAuthenticationProvider(); var mapper = new SimpleAuthorityMapper(); mapper.setConvertToUpperCase(true); authenticationProvider.setGrantedAuthoritiesMapper(mapper); return authenticationProvider; } @Bean @Override protected SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionAuthenticationStrategy() { //6 return new RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategy(new SessionRegistryImpl()); } } |
There are a few things to note:
@KeycloakConfiguration– this metadata annotation provides all annotations that are needed to integrate Keycloak in Spring Security (e.g. for enabling Spring Security or configuring component scanning);KeycloakWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter– by extending this class we gain a useful base class for creating a WebSecurityConfigurer instance secured by Keycloak;SecurityConfig::configure– we’re going to overwrite the basic Spring Security behaviour, first by calling the parent implementation and then by adding our own csrf and endpoint protection config;SecurityConfig::configureGlobal– furthermore, we have to register the KeycloakAuthenticationProvider with the authentication manager;SecurityConfig::getKeycloakAuthenticationProvider– my auxiliary method for customising the authentication provider. Namely, I’m providing a simple one-to-one GrantedAuthoritiesMapper which adds theROLE_prefix and converts the authority value to upper case (e.g. achief-operating-officerrole from Keycloak realm becomesROLE_CHIEF-OPERATING-OFFICERin my Spring Boot app);SecurityConfig::sessionAuthenticationStrategy– the session authentication strategy bean has to be of typeRegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategyforpublicorconfidentialapplications (NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategyforbearer-onlyapplications).
Test basic Keycloak configuration for Spring Security
Although I haven’t restricted access to any endpoint in my API, I’m still going to test the current setup. I’m going to enable the DEBUG log lever for security by adding the following property to my application.properties file:
|
1 |
logging.level.org.springframework.security=DEBUG |
As a result, I can verify the configuration details and see that Keycloak filters are present in the filter chain:
|
1 2 3 4 |
… DEBUG 12469 --- [main] edFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource : Adding web access control expression [permitAll] for any request INFO 12469 --- [main] o.s.s.web.DefaultSecurityFilterChain : Will secure any request with […, org.keycloak.adapters.springsecurity.filter.KeycloakPreAuthActionsFilter@439e3cb4, org.keycloak.adapters.springsecurity.filter.KeycloakAuthenticationProcessingFilter@31e76a8d, …] … |
Moreover, Spring Security doesn’t create a user password which would be its default behaviour without the Keycloak configuration.
At this point, my Spring Boot application is delegating authentication and authorization processes to Keycloak. However, I am still free to call the endpoints as they are not explicitly secured.
Secure endpoints
Next, I’m going to restrict access to the API endpoints by replacing anyRequest().permitAll() with the anyRequest().authenticated() line:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
… public class SecurityConfig extends KeycloakWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { super.configure(http); http … .authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated(); } |
After restarting the application, I can see in its logs that all endpoints are protected:
|
1 2 3 |
… DEBUG 13361 --- [main] edFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource : Adding web access control expression [authenticated] for any request … |
As a result, my Postman setup and Swagger UI config require additional configuration to allow me to make API calls.
Update tests after configuring Spring Security to use Keycloak
Configuring security in a project will break existing Spring MVC tests. Therefore, below you will find some details that require updating.
Disable Keycloak in tests and use plain Spring Security
I don’t want to clutter tests with the configuration of an external authorization service. Therefore, I’m going to configure my Spring MVC tests to use Spring Security instead of Keycloak. For full instructions on how to apply a different security configuration in tests, see the Keycloak with Spring Boot #2 – Spring Security instead of Keycloak in tests post.
Mock an authenticated user
Fortunately, Spring Security provides the @WithMockUser annotation. We can apply it to a specific test or an entire class. In the following example test method, we can see how to use this annotation in a single test while keeping the default user data:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
@Test @WithMockUser void shouldReturnAllProducts() throws Exception { ProductResponse productResponse = productResponseProvider.full(); String expected = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(List.of(productResponse)); when(apiFacade.findAll()) .thenReturn(List.of(productResponse)); mvc.perform(get("/api/products") .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(content().json(expected)); } |
Additionally, we can customise the username, password, roles and authorities (the latter two are exclusive) that our mocked user will receive:
|
1 |
@WithMockUser(username = "thomas", password = "test", roles = {"EDITOR"}) |
Include csrf protection
As you may have noticed, my security configuration uses csrf protection. Therefore, I have to add the SecurityMockMvcRequestPostProcessors::csrf method that automatically populates a valid CSRF token in my POST request:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
@Test @WithMockUser void shouldSaveNewProduct() throws Exception { ProductRequest newProduct = productRequestProvider.full(); ProductResponse savedProduct = productResponseProvider.full(); String expected = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(savedProduct); when(apiFacade.save(newProduct)) .thenReturn(savedProduct); mvc.perform(post("/api/products") .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON) .content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(newProduct)) .with(csrf())) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(content().json(expected)); } |
Read more on integrating Spring Security with Keycloak
- Keycloak with Spring Boot #2 – Spring Security instead of Keycloak in tests
- Keycloak with Spring Boot #3 – How to authorize requests in Swagger UI
- Kecloak in Docker #7 – How to authorize requests via Postman
- Securing Spring Boot with Keycloak documentation for Keycloak 16.1.1 and Keycloak 17.0.0.
- Keycloak in Docker #1 – How to run Keycloak in a Docker container article.
- Spring Security and Keycloak to Secure a Spring Boot Application – A First Look
