Having automated database migrations will significantly ease managing schema development. With Spring Boot support we can effortlessly handle versioned SQL scripts.
What we are going to build
I have an example Spring Boot project that is configured to connect to a PostgreSQL database run from a docker container. I’m going to add Flyway to this project and use migrations to create tables based on my entities. I will write migrations in SQL. Every file will enclose a distinct set of commands updating the database schema to a newer version.
You can learn how to instantiate a database in a container in the Set up a PostgreSQL database with Docker post.
You can learn how to connect a Spring Boot project with a PostgreSQL database in the Add a PostgreSQL database to your Spring Boot project post.
You can find the example project used in this post in the spring-boot-postgres-flyway repository.
Architecture overview
Our example REST API has only one entity – Cookie. The application relays on a PostgreSQL database that can be instantiated using the docker container that is included in the project.
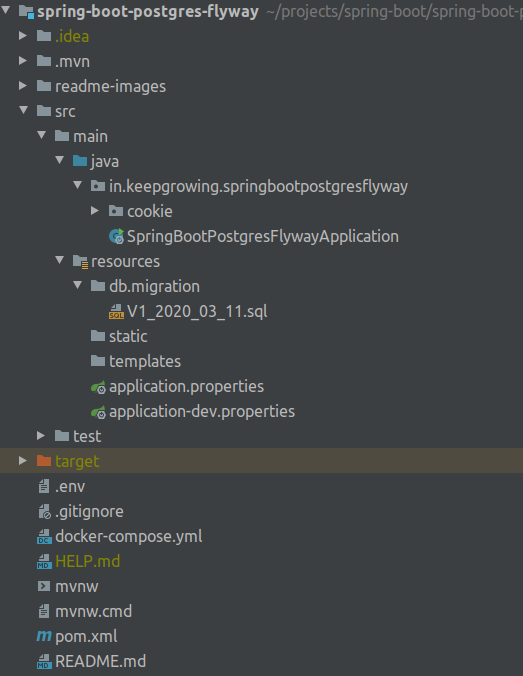
You can see the project directory tree on the image below:
Requirements
- We are working on a
Spring Boot 2.2.5project with theWebandJPAdependencies. You can read about setting up a similar project with Spring Initializr in How to create a new Spring Boot Project post.
- A PostgreSQL database. You can use the container that is included in the repository and presented in the Setup a PostgreSQL database with Docker article. You will need Docker Engine – Community with Docker CLI for that.
Include the Flyway dependency
Add the dependency for the Flyway core driver to your pom.xml file:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
<!--pom.xml--> … <dependency> <groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId> <artifactId>flyway-core</artifactId> </dependency> … |
Create migrations
Migration files are detected automatically through filesystem and Java classpath scanning at runtime. You can specify a custom location of those files:
Once you have configured the
https://flywaydb.org/documentation/migrations#discoverylocationsyou want to use, Flyway will automatically pick up any new SQL migrations as long as they conform to the configured naming convention.
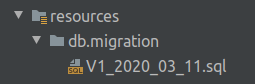
I created the db and migration directories in the resources folder, as that is where Flyway will be looking for my migrations by default:
You don’t have to write the first migration by hand
We can obtain a ready to use SQL by utilizing Hibernate features for saving the DDL script into a file. Read the Save Hibernate DDL schema to a file post to learn how you can save time when creating the first migration.
If you have more entities that one and there are relations between them, writing the script manually may be cumbersome. In my project, the generated file looks like this:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
-- schema.sql create table cookie ( id bigserial not null, flavour varchar(255), primary key (id) ) |
Once you’ve verified the prepared code you can move the file to the resources/db/migration or any other location that you had specified in application properties.
Naming strategy
Furthermore, we have to change the file name so it adheres to the naming convention. I decided to include the date of every migration in the Version part, so in my case the first migration that was created on March 11th 2020 is called V1_2020_03_11.sql. The Description part is optional and I decided to not include it for the sake of brevity. Whatever your strategy is, make sure that it’s uniformly accepted and used by all members of the team.
Flyway allows us to decide how to handle files that breaks the naming strategy:
The configuration option
https://flywaydb.org/documentation/migrations#namingvalidateMigrationNamingdetermines how Flyway handles files that do not correspond with the naming pattern when carrying out a migration: iftruethen Flyway will simply ignore all such files, iffalsethen Flyway will fail fast and list all files which need to be corrected.
Remove conflicting properties
We no longer want Hibernate to create the tables when the application starts. Remember to remove properties like this one:
|
1 |
spring.jpa.properties.javax.persistence.schema-generation.database.action=create |
or the following one:
|
1 |
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create |
In my example I am using a database run in a Docker container, so I removed the volume to make sure that the first migration will generate the schema. Then I started the container with the following command:
|
1 |
$ docker-compose up -d |
If you were using an in-memory database, you don’t have to worry with dropping it.
Start the application
On application startup all new migrations will be executed automatically.
Verify logs
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
INFO o.f.c.internal.database.DatabaseFactory : Database: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/springbootpostgresflyway (PostgreSQL 9.6) INFO o.f.core.internal.command.DbValidate : Successfully validated 1 migration (execution time 00:00.006s) INFO o.f.c.i.s.JdbcTableSchemaHistory : Creating Schema History table "public"."flyway_schema_history" ... INFO o.f.core.internal.command.DbMigrate : Current version of schema "public": << Empty Schema >> INFO o.f.core.internal.command.DbMigrate : Migrating schema "public" to version 1.2020.03.11 INFO o.f.core.internal.command.DbMigrate : Successfully applied 1 migration to schema "public" (execution time 00:00.016s) |
If you rerun the app without any new migrations, you will see:
|
1 2 3 |
INFO o.f.core.internal.command.DbValidate : Successfully validated 1 migration (execution time 00:00.008s) INFO o.f.core.internal.command.DbMigrate : Current version of schema "public": 1.2020.03.11 INFO o.f.core.internal.command.DbMigrate : Schema "public" is up to date. No migration necessary. |
Verify databse tables
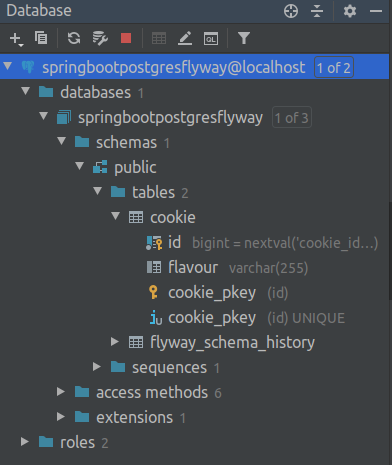
You can see the database schema on the screenshot taken from my IntelliJ on the image below:
Keep track on migrations
Flyway clearly marks which migrations were already applied. Therefore you always know which scripts are going to be recognized as “new” and run against the database. This is the purpose of the flyway_schema_history table that was automatically created in our database. The table is described in the documentation with these words:
You can think of this table as a complete audit trail of all changes performed against the schema. It also tracks migration checksums and whether or not the migrations were successful.
https://flywaydb.org/documentation/migrations#schema-history-table
In my project the table contains the following record:

Verify the status
Migrations that were detected by Flyway’s filesystem are initially pending. My first migration is marked as success in the history table shown above. That means it was applied to my database without issues. In case of a failure there are two possible outcomes:
(1) When the migration fails and the database supports DDL transactions, the migration is rolled back and nothing is recorded in the schema history table.
https://flywaydb.org/documentation/migrations#migration-states
(2) When the migration fails and the database doesn’t support DDL transactions, the migration is marked as failed in the schema history table, indicating manual database cleanup may be required.
The other available states are: undone, future and outdated. Check out the Migration states documentation for more details.
Conclusion
The work done in this project is contained in the commit 7054d3618811346871ba97ad153f7f185d695319.
Now every time my database structure requires modification I can write updates in SQL and save them as a new migration. I always now on which version of the database I’m currently working and which scripts haven’t been applied to my schema. When new developers join my team the up to date version of the database is automatically created on their machines when they start the app.
You can read more about reasoning behind migrations in the Flyway docs.
An alternative to Flyway
Another popular tool for managing database changes is Liquibase. Similarly to Flyway it also can be added to a Spring Boot project with a dedicated Maven dependency – liquibase-core.
Photo by Kristopher Roller on StockSnap
