The springdoc-openapi library allows us to automatically generate an OpenAPI specification for our rest API built with Spring Boot. This specification is also useful when we need a Swagger documentation or we want to automate client code generation.
You can find example projects with springdoc-openapi in the spring-boot-angular-scaffolding or spring-boot-swagger-ui-keycloak repositories.
Add Maven dependencies
First, we are going to add the Maven dependencies for the springdoc-openapi-ui and springdoc-openapi-data-rest libraries (part of the springdoc-openapi project) to our pom.xml:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
<properties> <springdoc.version>1.5.9</springdoc.version> <!-- … --> </properties> <!-- … --> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springdoc</groupId> <artifactId>springdoc-openapi-ui</artifactId> <version>${springdoc.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springdoc</groupId> <artifactId>springdoc-openapi-data-rest</artifactId> <version>${springdoc.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- … --> </dependencies> |
As a result, we now have an automatically generated OpenAPI specification for our Spring Boot project and all its REST endpoints. Just start the app and visit http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs:

Documentation via Swagger UI
All you need to do is visit the http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html url and verify the generated documentation:
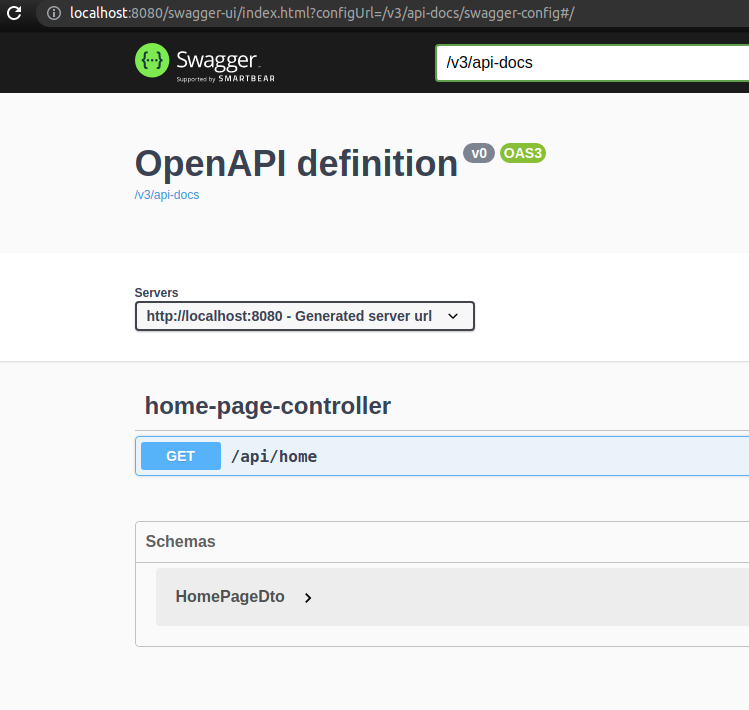
As we can see, the generated specification and documentation contain only basic information and use the default naming convention. We’re going to customize it with some additional configuration.
Add custom configuration
The code used below is available in the spring-boot-angular-scaffolding repository.
Customize specification with annotations
If we want to avoid implementation details leaking through names like HomePageDto or home-page-controller, we can customize those names with annotations. We’re going to use @Schema on our HomePageDto object:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.media.Schema; … @Schema(name = "Home") public class HomePageDto { … |
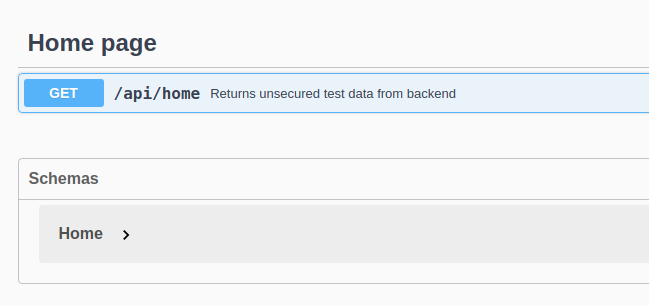
Next, we’re going to change the controller name and add a description for our example endpoint:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation; import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag; … @Tag(name = "Home page") public class HomePageController { @GetMapping @Operation(summary = "Returns unsecured test data from backend") public ResponseEntity<HomePageDto> getHomePageData() { … |
As a result, we will see a more friendly version of our docs when running the app again:
Add project info
Furthermore, we can add some project details to the generated specification. Fortunately, we have project name, description and version already defined in our pom.xml file:
|
1 2 3 |
<name>backend</name> <description>The backend module built with Spring Boot</description> <version>2.0.1</version> |
Thanks to the Automatic Property Expansion feature we can use the existing build configuration. Let’s create custom properties in our application.properties file and assign their values:
|
1 2 3 |
openapi.project-title=@project.name@ openapi.project-version=@project.version@ openapi.project-description=@project.description@ |
Following the Spring Boot documentation on Externalized Configuration, specifically the Type-safe Configuration Properties chapter, we’re going to create the OpenApiProperties class:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
package in.keepgrowing.springbootangularscaffolding.shared.config.openapi; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Getter; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConstructorBinding; @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "openapi") @ConstructorBinding @AllArgsConstructor @Getter public class OpenApiProperties { private final String projectTitle; private final String projectDescription; private final String projectVersion; } |
Finally, we can use those properties in our OpenAPI configuration class. Additionally, we can specify the license of the project as well:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
package in.keepgrowing.springbootangularscaffolding.shared.config.openapi; import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.OpenAPIDefinition; import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.OpenAPI; import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.info.Info; import io.swagger.v3.oas.models.info.License; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @OpenAPIDefinition @AllArgsConstructor public class OpenApiConfig { @Bean public OpenAPI customOpenAPI(OpenApiProperties properties) { return new OpenAPI() .info(getInfo(properties)); } private Info getInfo(OpenApiProperties properties) { return new Info() .title(properties.getProjectTitle()) .description(properties.getProjectDescription()) .version(properties.getProjectVersion()) .license(getLicense()); } private License getLicense() { return new License() .name("Unlicense") .url("https://unlicense.org/"); } } |
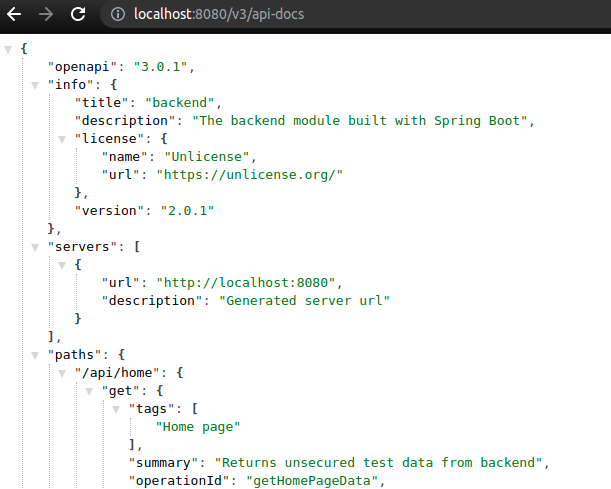
Consequently, the swagger-ui page will include the specified project details:

Obviously, we will see all those changes in the specification as well:
Springdoc-openapi modules
It’s important to realize that in this example we added only one springdoc-openapi module to our project – Spring Data Rest. However, Springdoc comes with multiple modules, offering support for Spring Security, Hateoas, Kotlin etc.
Enable csrf support
Springdoc supports protecting endpoints against CSRF attacks. Update the springdoc-openapi dependencies in your pom.xml file to version 1.6.6 for working support for CSRF configuraiton. Then add the following property to your application.properties file:
|
1 2 3 |
# application.properties … springdoc.swagger-ui.csrf.enabled=true |
As a result, Swagger UI will successfully execute calling POST or DELETE endpoints with csrf enabled in Spring Boot.
Specification in the yaml format
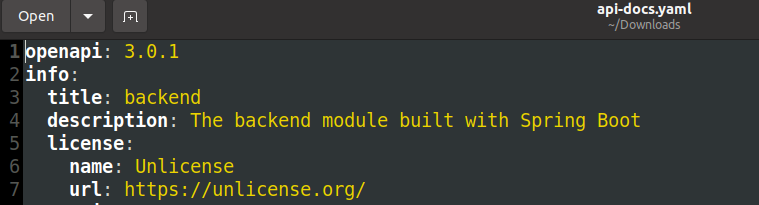
Another springdoc-openapi feature worth mentioning is the ability to generate the API specification as a yaml file. We can download the api-docs.yaml file under the http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs.yaml url:
Learn more on documenting Spring Boot API
- Springdoc-openapi docs
- Springdoc-openapi Demos
- Migrating from SpringFox
- How to set up Spring Boot app documentation with Springfox
Photo by Taryn Elliott from Pexels
